Unlocking the full potential of AI-native 6G through standards
7 March 2025

Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to become pervasive throughout the telecommunications ecosystem. Even today, AI is transforming workflows, processes, and products in all industries. As just one example of many, according to a McKinsey 2025 study, telco operators expect not less than 20% cost savings across all business functions. This transformation is fueled by rapid advancements in machine learning and AI models capabilities and architectures, unprecedented access to high-performance hardware for training and inferencing, as well as access to vast amount of data accompanied by methods for synthetic data generation for training and further improving AI model capabilities.
AI opportunities are documented daily in the business press, with enormous investments being made in data centers as enterprises race to be the leaders in this field. It has even become a strategic interest at the nation-state level and is at the heart of national industrial strategies. As we plan for the 6th generation of mobile cellular networks (6G), we need to understand the urgency that faces us. AI will be instrumental in shaping 6G, which will be the first generation of cellular networks truly designed with AI at its core. Despite the many players racing to define our AI future, the telco industry has a unique opportunity to set the pace with AI-native 6G.
Figure 1. 6G cellular networks will be built on AI
As the first generation of mobile cellular networks with AI in its DNA, AI and machine learning (ML) will be integrated into all domains and layers of the 6G system, from devices to the RAN, core network, and orchestration/management domain. To achieve maximum cohesion and efficiency, this must be done in a systematic way ensuring interoperability, predictability and availability of AI resources at all levels of the system, while also allowing for maximizing agility to adopt new AI-driven technologies. Availability of key AI enablers will allow all stakeholders to build and deploy high-quality, innovative AI models and solutions:
- Access to data for training and inference
- Access to compute infrastructure for inference and training
- Support for AI and ML end-to-end lifecycle management.
Standards will have a decisive impact on the strength and innovation capabilities of the 6G ecosystem. They will not only ensure trust by meeting critical regulatory, security and privacy aspects, but also, to enable seamless and resource-efficient integration of diverse solutions and technologies. The goal is to create an ecosystem for AI and 6G that lays the foundation for a decade of new use cases, while ensuring the integrity of our communications systems. Customers will be the ultimate beneficiaries. AI will help to provide them with a wider array of innovative services and applications, enhancing their overall experience, and retaining the historical trust that they have long had for telco services.
This article explores the key standardization enablers for an AI-native 6G. We take a holistic approach across all network and system domains, drawing upon the lessons learned from 5G-Advanced. This holistic approach will minimize functional overlaps between different system domains, ensuring a streamlined and efficient network architecture.
Creating value with standardization of AI enablers
For 6G the goal is to develop an approach to AI that reflects business priorities, not hype. AI has enormous potential to add value to 6G. AI-native 6G will be a pivotal force in driving revenue, growth, performance, and reducing operational costs. It represents a fundamental shift, whether for optimizing network performance, enabling new business models, or providing tangible value to CSPs and industry verticals. In the case of intent-based cognitive automation, the value AI provides can be as high as 90% faster detection and resolution of network issues compared to manual methods. Similarly, AI powered energy-saving provides 10–20% RAN energy savings while promising more improvement to come.
Figure 2 and the following table illustrate further the value-creation potential of AI-powered solutions in 6G. For example, AI agents have the potential to fundamentally transform the way humans and machines get tasks done: AI agents are autonomous components powered by generative models that analyze and act on contextual information towards the fulfilment of a given intent. AI agents can accomplish specific tasks leveraging capabilities such as planning and reasoning, performing reflections, and using external tools. To realize their full potential, agentic AI systems need access to contextual data relevant for the specific task at hand, as well as mechanisms for orchestration and collaboration across the system.
Beyond automation and efficiency, AI will play a strategic role in making networks capable of continuously and autonomously optimizing for changes in traffic, radio and user behavior. It will speed service delivery, improve customer experiences, enhance decision making, and unlock new revenue streams. It will also support many new use cases and applications such as generative AI, agentic AI, robotics and immersive extended reality (XR) by providing edge-based AI-powered services tailored to the user’s needs.
Figure 2: Value creation opportunities using AI enablers
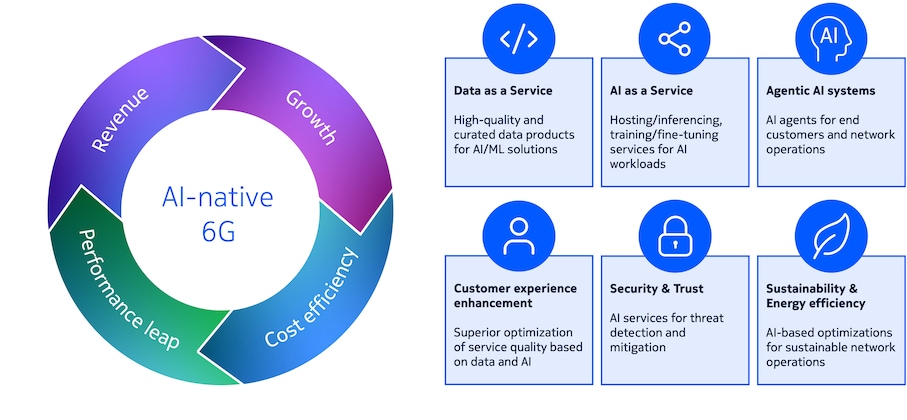
Value creation opportunities |
AI enablers |
|---|---|
Data as a service |
|
AI as a service |
|
Customers experience enhancement |
|
Security and trust |
|
Sustainability and energy efficiency |
|
Agentic AI systems |
|
Not all the enablers for AI need to be standardized. However, for a thriving ecosystem which is future proof to cover applications and use cases not foreseen, a holistic and balanced approach is needed. It should identify the key enablers in the AI framework that must be standardized to allow for interoperability.
Evolving AI use from 5G-Advanced to 6G
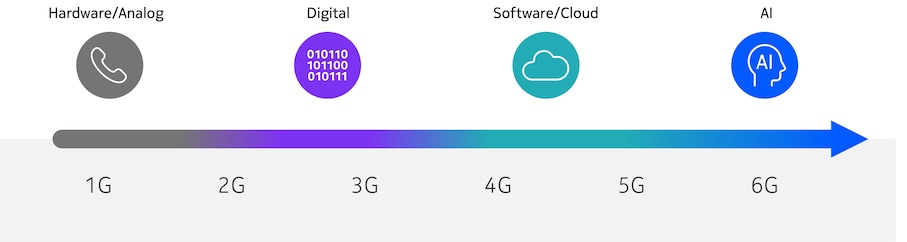
The groundwork for AI-enhanced connectivity and intelligent network operations was laid in 5G-Advanced (5G-A) with support for AI training, testing, validation and monitoring. As illustrated in Figure 3, AI enablers will need to support functions at all layers of the network including network components, collaborative solutions across components and domains, as well as over-the-top (OTT) solutions. This must be done in a flexible and future-proof way that allows for innovation and agile adoption of new AI capabilities.
Figure 3. The evolution towards AI-native 6G in standards
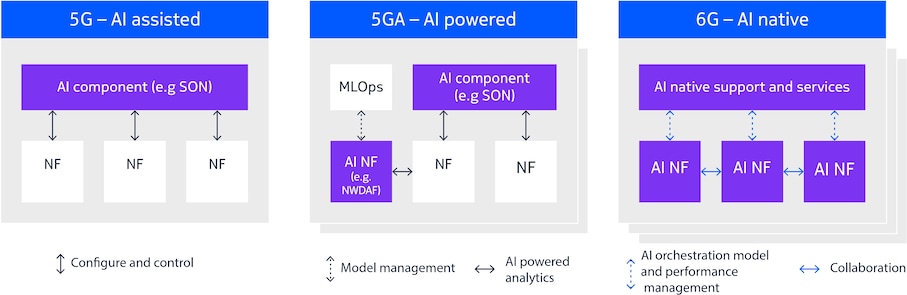
The evolution of standards addressing AI/ML from 5G to 6G mirrors the gradual, then rapid, increase in AI/ML model capabilities. Starting with insular components like SON in 5G (and earlier generations), the shift accelerated following the ChatGPT moment, highlighting AI's vast potential in RAN and radio. This progression culminates in a fully AI-native 6G, where AI/ML is integrated into every layer and domain of the system.
In many aspects the AI/ML features in 5G-Advanced 3GPP standards form the foundation for 6G, such as the Release 18 and 19 study and work items on AI in radio as well as the introduction of Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF) and its further generalization and extensions with the Data Collection Coordination Function (DCCF) in 5G core. The lesson from 5G and 5G-Advanced is that standardized AI enablers should be based on consistent design principles across all network domains, and they should avoid duplicated functionalities and complexities for implementation.
AI-native 6G design principles
AI-native principles and requirements are not an overlay. They must be baked in from day one in all phases from design and deployment to operations, as shown in Figure 4. Starting at the planning stage, the network must be capable to handle all types of AI applications, workloads, and data requirements with the necessary infrastructure. AI components must be built into hardware and software and integrated during deployment—not as aftermarket modifications.
Figure 4. Design principles and objectives of AI-native 6G
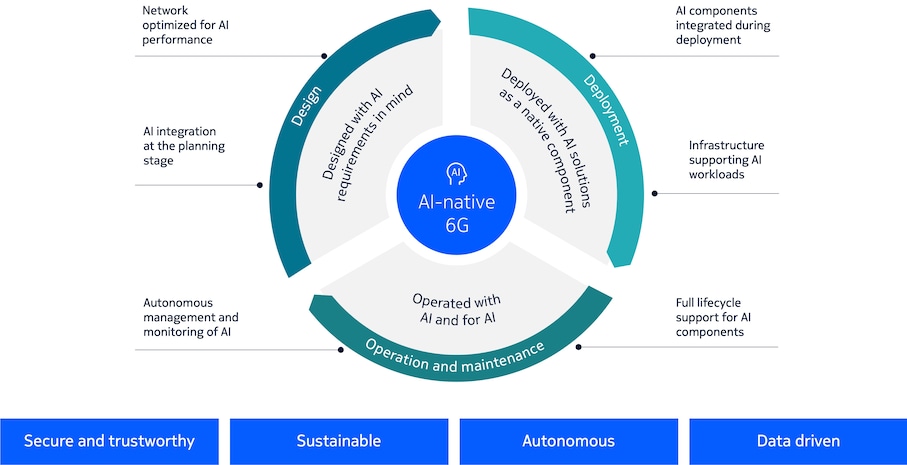
The network architecture must be optimized to support AI workloads, removing bottlenecks that might affect latency and QoS requirements. This includes the physical and virtual compute infrastructure of the network needed to support AI training, fine-tuning and inferencing workloads. The full lifecycle of AI components needs to be supported to ensure applications can be developed, deployed, tested and maintained according to MLOps methodologies.
The AI-native 6G design must reflect the following principles:
- To ensure security and trustworthiness, AI solutions are explainable and predictable in operation, as well as robust against internal and external threats
- AI-native networks are sustainable, energy efficient and monitorable to ensure compliance with zero-emission and CO2 neutrality
- AI lifecycle management is fully autonomous using closed loops for scalable deployments and reducing the burden of manual configuration and monitoring
- Data can be collected, managed and transformed from all layers and domains of the network, including devices.
An AI-native 6G architecture blueprint
To meet these principles the following fundamental capabilities need to be introduced to provide the necessary resources for AI:
- AI-native enablement capabilities for training, inferencing and cross-domain orchestration of end-to-end AI solutions, model storage and cataloguing
- Data prosumer (producer/consumer) capabilities supporting all steps of the AI lifecycle.
These capabilities provide a scalable foundation for seamless design, deployment and operation of AI solutions and are utilized by AI components across all network domains and functions. They avoid the need to manually adjust the network configurations every time a new AI based solution is deployed, and they ensure continuous autonomous pipelines for data and MLOps.
Figure 5. Architectural blueprint for AI-native 6G

AI-native enablement capabilities
A common definition of AI enablement capabilities allows resource- and cost-efficient implementation across the network. Capabilities can also be exposed to customers as a service for additional value creation, such as AI edge applications. Furthermore, a common definition of interfaces and services can foster competition among third-party providers of these services for further cost savings. Drilling down on the capabilities shown above, we foresee a need for the following:
- Data Catalogs store metadata for AI/ML tasks, tracking data quality, provenance, and preventing data poisoning. They also manage role-based access control (RBAC) for secure data handling.
- Compute and storage for AI includes computing resources for model training and serving, along with specialized storage for hosting, tracking, and securing models and their training datasets.
- (re)Training, validation and testing provide essential functions for model generation, including hyperparameter tuning, assessment, and evaluation.
- Inference engines provide the necessary functionalities to run models in operational environments, ensuring they meet SLAs and requirements such as latency and prediction quality.
- AI/ML model catalogs store metadata on models and their training data, track provenance, and enforce role-based access control.
- Large model farms for larger models such as LLMs, which may have to be hosted within or outside the service provider’s cloud.
- AI orchestration manages AI data and ML pipelines with intent-based interfaces, mapping requirements to blueprints. It includes lifecycle management (LCM) of ML models, performance monitoring, and multi-inference support like distributed learning and mixture of experts.
- Cloud-edge orchestration enables secure deployment of data and ML pipelines across multiple cloud resources, including edge, metro, and central clouds from various providers.
- Network digital twins (NDT) model network behavior with high fidelity to train ML models. NDT may themselves use ML models, utilizing AI/ML enablement functionalities.
Data prosumer capabilities
Data-related functions are fundamental to AI enablement across the network. Enablement functions either produce or consume data, sometimes both. For example, models, training data, measurements and counters produce data, while inferencing, monitoring and inference quality tracking, consume it. We identify the following data-related capabilities:
- Data abstraction functions help make data access seamless and uniform, regardless of its origin or how it’s collected
- Metadata is required to manage the collection, storage and security of data, from what it is and where it comes from to how it is collected and who can access it and why
- Data operations and products implement access and process data, making data available in a variety of forms, whether it’s raw, processed, curated or annotated
- Synthetic data generation of data to fill the measurement data gap and provide additional training data for improved model performance.
In summary, both AI enablement and data prosumer capabilities provide the essential resources through harmonized APIs to build powerful AI-enabled solutions for increased revenue and growth, better performance, and improved efficiency. Standardization needs to ensure that key enablers such as data collection, processing, management and exposure are specified based on common principles across different working groups in 3GPP to avoid duplicate and incomplete functionalities across the system, while considering domain-specific requirements.
Conclusion and outlook
For 6G to be truly AI native and capable of powering AI use cases of every kind, it has to be more than an overlay or add-on to the 6G system. AI-powered components need to be built into the architecture and be scalable, secure and ensure privacy. Standards must ensure the interoperability (e.g. that device conformance and performance criteria are met with and without AI in consistent and predictable manner) of these components in a truly open way that ensures competitive value creation and flexibility for faster innovation cycles.
To this end, an AI-native network must be architected with AI enablement and data prosumer capabilities. As outlined, the interactions among AI solutions in different domains is enhanced by means of the functions provided in the enablement capabilities. In addition, the AI enablement and data prosumer capabilities are exposed to different consumer entities from different domains in the network to support the pervasive presence of AI-driven solutions. Only this holistic approach will truly realize the promise of 6G and provide AI-powered communications services that meet the needs of tomorrow.
Read more
About Nokia
At Nokia, we create technology that helps the world act together.
As a B2B technology innovation leader, we are pioneering networks that sense, think and act by leveraging our work across mobile, fixed and cloud networks. In addition, we create value with intellectual property and long-term research, led by the award-winning Nokia Bell Labs.
With truly open architectures that seamlessly integrate into any ecosystem, our high-performance networks create new opportunities for monetization and scale. Service providers, enterprises and partners worldwide trust Nokia to deliver secure, reliable and sustainable networks today – and work with us to create the digital services and applications of the future.
Media inquiries
Nokia Press Office
Email: Press.Services@nokia.com
Follow us on social media