5G myths debunked
Take the quiz
5G facts and myths
5G facts and fiction, it’s time to debunk some 5G myths. From cloud gaming, low latency and energy efficiency, the need to find the truth behind this topic has never been more crucial. Like every new technology, certain myths arise that don’t stand up to more scrutiny. Take the 5G facts and fictions quiz.
#1 5G could be used in professional audio broadcasting for in-ear monitoring for musicians in live performances
In recent testing Nokia together with Sennheiser have demonstrated the capability for 5G to support a latency of 4ms from microphone to the in-ear monitor musicians use during live performances. The programme making and special events (PMSE) industry could utilize a private 5G wireless network at large venues such as stadiums and concert arenas.
#2 5G can be used to connect machines in a mine 1000 meters below ground
By deploying a private wireless network inside the mine, it allows workers operating the machines to monitor operations through wirelessly connected video cameras. This can help in improving safety and efficiency of operations in these hazardous work environments.

Industry
Mining
#3 5G will allow for teleportation
Not quite yet… but 5G ultra-low latency will allow for haptic feedback, for example haptic gloves rendering the feel and touch of remote objects. Coupled with VR this will allow remote manipulation of machines to handle hazardous materials, basically being transported anywhere in a snap of finger!
#4 With 5G, farmers can save water and improve harvests
5G can manage up to 1 million low-power connected devices per square kilometer. Connected sensors in the fields can report and analyze in real-time the water needs with a fine granularity and trigger optimized and automated watering.
#5 5G today can determine the location of a device within 1m outdoors
Without the assistance of other technologies (such as GPS), 5G today can support device location to within 50m. In future developments it will be able to support <20cm and eventually <1cm indoors and <10cm outdoors. This will be necessary to support a variety of advanced application in control of robotics in industrial environments to fully autonomous systems.
#6 5G can support connectivity while travelling up to speeds of 500km/h
Mobility is the maximum speed the user device is travelling at, and where a defined level of service can be achieved. The different classes of mobility for 5G are:
- Pedestrian: 0 km/h to 10 km/h
- Vehicular: 10 km/h to 120 km/h
- High speed vehicular: 120 km/h to 500 km/h, which is mainly envisioned for high speed trains!
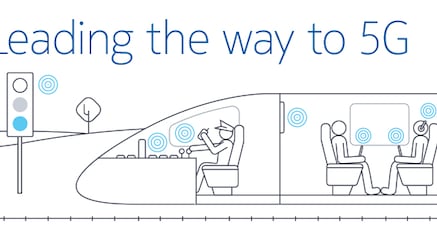
Infographic
FRMCS/5G for railway operations
#7 5G is less secure than 4G
From identifying and authenticating devices, to the interconnection of different mobile networks and protection of the data transmitted, there are new capabilities to conceal device identities and integrity of the information transferred. By applying encryption procedures and modifying radio transmission parameters you can reduce the risk of a connection being compromised.
Keen to learn more?
Want to debunk some more 5G Myths?











