Business readiness for 5G

The role 5G can play in helping companies optimize their operations and drive innovation could not be clearer. Bell Labs Consulting’s research outlined in the previous chapter underlines the potential for organizations to use 5G to leapfrog multiple stages of their digital transformation. But while 5G might be ready for business, how ready is business for 5G?
In addition to the research by Bell Labs Consulting, we also conducted a study into how prepared businesses are to make the most of the opportunity ahead.
The study found that there is a gap between intentions and actions when it comes to any kind of 5G deployment for many companies. While 86% of decision makers said they have some kind of strategy for 5G, only 15% are currently investing in its implementation.
The fact that another 57% plan to invest within the next five years suggests companies are at the beginning of what will be a lengthy runway on 5G deployment, as they scope use cases and identify necessary resources.

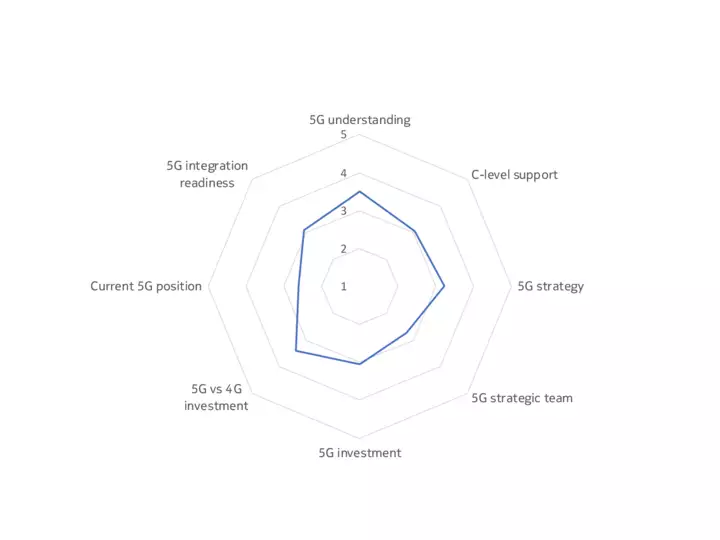
The Nokia 5G readiness scale
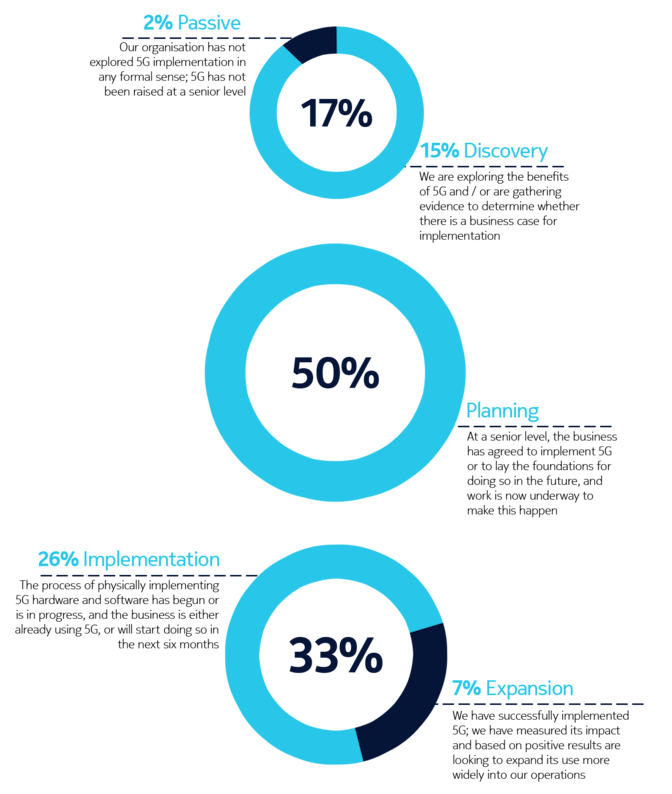
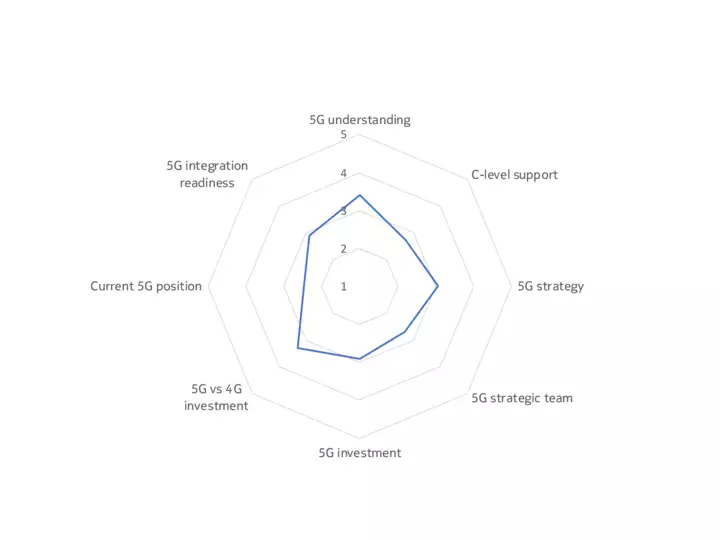
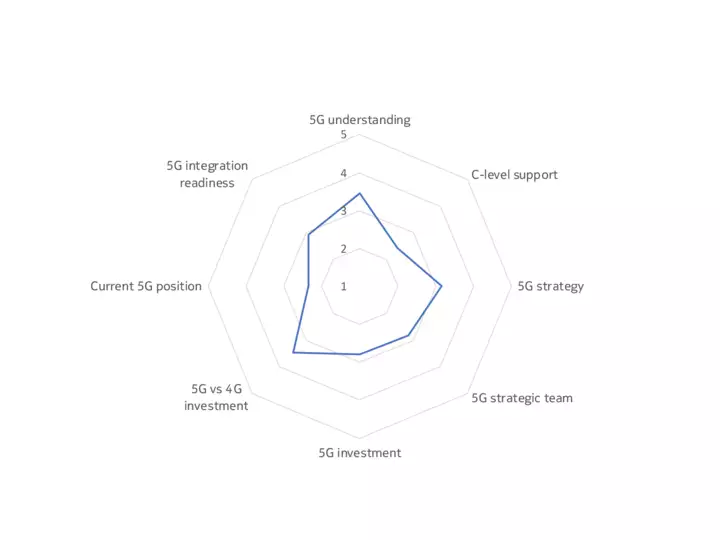
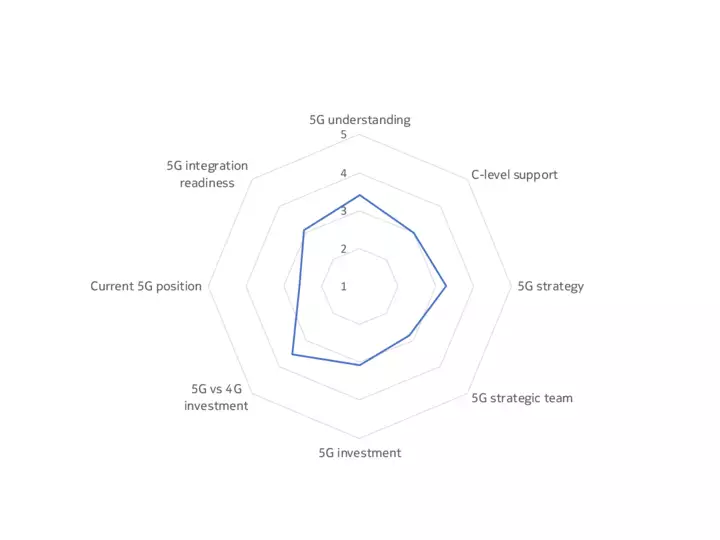
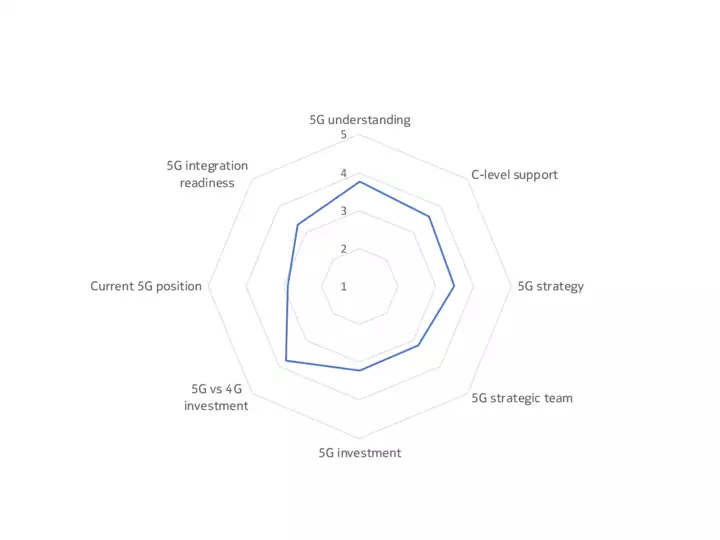
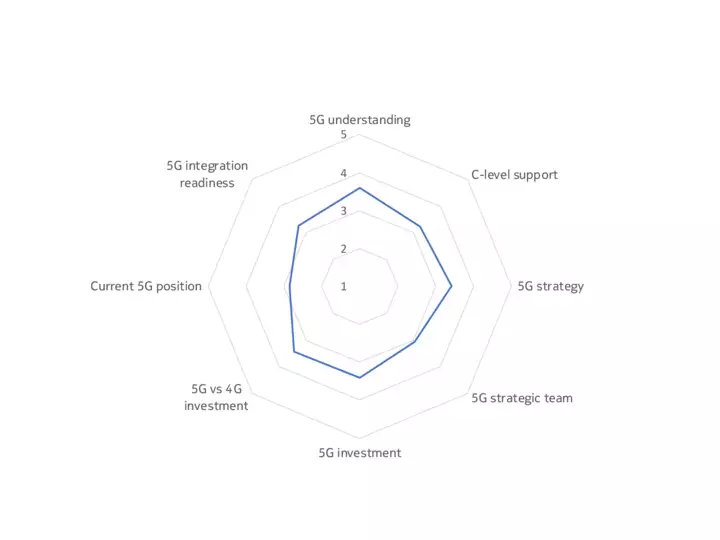
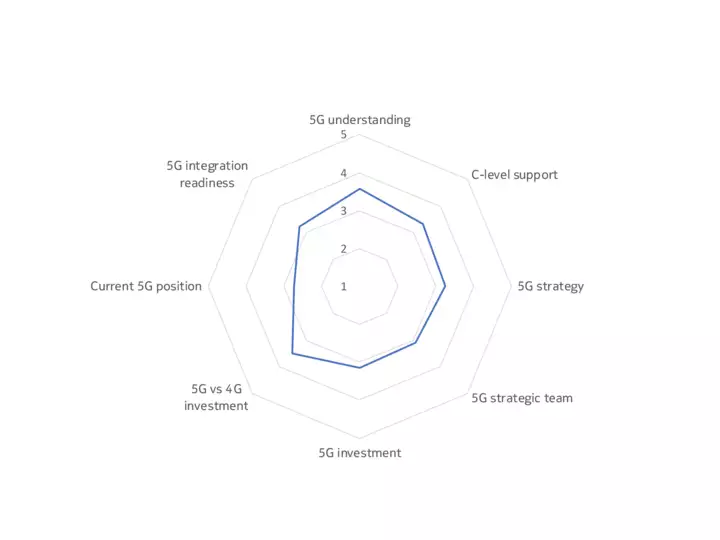
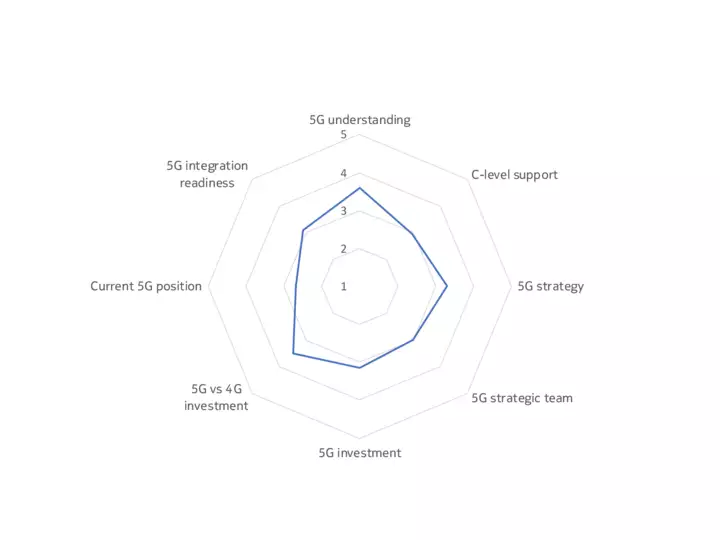
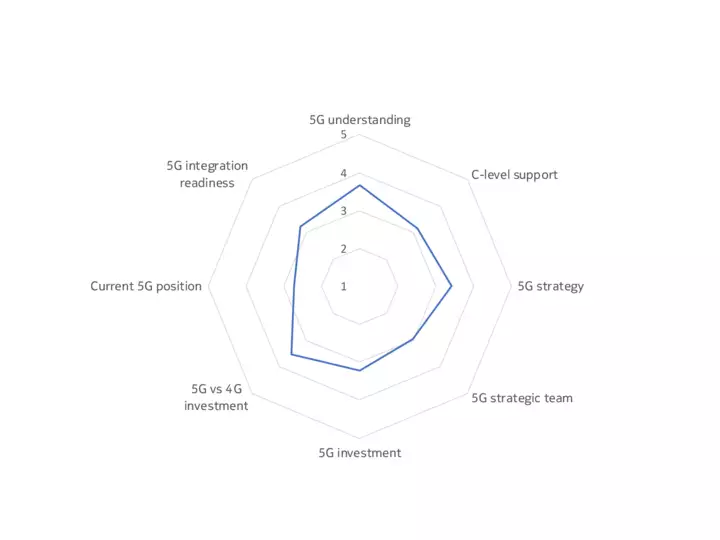
The upshot is that, while some companies, sectors and markets are advanced in their 5G preparations, most are at an intermediate point between initial planning, trials and deployment. Our 5G Business Readiness Model shows that 50% of companies are currently in the planning stage, suggesting they are at the midway level on 5G readiness. Meanwhile, 26% are at the Implementation stage, while 7% are now expanding their deployments – a phase we would describe as 5G mature, meaning a company has started to leverage 5G in at least one of its many use cases. Conversely, 17% are either in the Passive or Discovery phase, showing low 5G maturity.
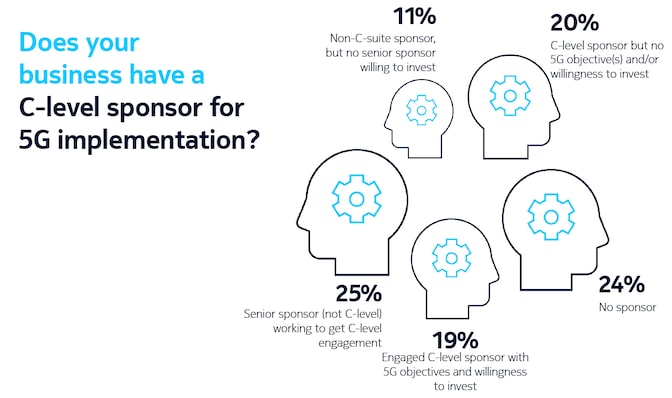
Findings underpinning the model included that only a third of decision-makers have a dedicated team for 5G within their organizations, and just one in ten of the technology buyers surveyed said their organization is fully resourced for 5G (across budget, personnel, software and hardware).
The survey also showed some distinct regional and industry variations. While 13% of organizations in Saudi Arabia and 12% in the United States rated as 5G mature, fewer than one in 20 were classed as such in Germany (3%), Finland (2%) and the UK (4%).
Take a look at the mastery model below to see how organizational readiness for 5G varies by sector and geography.
The five stages of 5G maturity
The five stages of 5G maturity
Passive: the business has not explored 5G implementation in any formal sense; 5G has not been raised at a senior level
Discovery: the business is exploring the benefits of 5G and / or are gathering evidence to determine whether there is a business case for implementation
Planning: at a senior level, the business has agreed to implement 5G or to lay the foundations for doing so in the future, and work is now underway to make this happen
Implementation: the process of physically implementing 5G hardware and software has begun or in progress, and the business is either already using 5G, or will start doing so in the next six months
Expansion: the business has successfully implemented 5G; it has measured its impact and based on positive results is looking to expand its use more widely into operations
Passive: the business has not explored 5G implementation in any formal sense; 5G has not been raised at a senior level
Discovery: the business is exploring the benefits of 5G and / or are gathering evidence to determine whether there is a business case for implementation
Planning: at a senior level, the business has agreed to implement 5G or to lay the foundations for doing so in the future, and work is now underway to make this happen
Implementation: the process of physically implementing 5G hardware and software has begun or in progress, and the business is either already using 5G, or will start doing so in the next six months
Expansion: the business has successfully implemented 5G; it has measured its impact and based on positive results is looking to expand its use more widely into operations




The benefits of 5G adoption
This relatively slow progress on 5G deployment could be limiting companies’ ability to boost their business performance, particularly in light of challenges arising from COVID-19. As well as assessing the 5G readiness of businesses across different countries and industries, our survey explored the relationship between 5G readiness and a company’s overall performance, confidence and technology strategy.
The findings suggest that 5G mature businesses have been better able to grow rapidly, maintain productivity, engage customers and instill confidence in employees. Notably:
5G mature companies are growing considerably faster than their peers: 49% of organizations in the Expansion phase companies and 37% in the Implementation phase said their organization achieved rapid growth last year, compared to 20% who classified as at the Planning phase, 11% in Discovery and 5% Passive.
Companies at the Expansion stage were the only sub-category to have experienced a net increase in productivity (+10%) following COVID-19, compared to Implementation (-3%), Planning (-15%) and Discovery (-40%).
Only 5G mature companies have been able to increase customer engagement (by 12%) during the pandemic, compared to no change for Implementation-stage organizations, -9% for companies at the Planning stage, -28% for organizations in the Discovery stage and -47% for Passive.
Across the board, only 22% of respondents said they have ‘total confidence’ in the ability of their organization’s leadership to cope with the impact of COVID-19, but that rises to 56% among those at the Implementation stage of 5G readiness, and 67% for those at the Expansion stage of 5G deployment.
Expectation vs reality: the anticipated impact of 5G by organizations yet to invest, and the actual impact felt by those who have
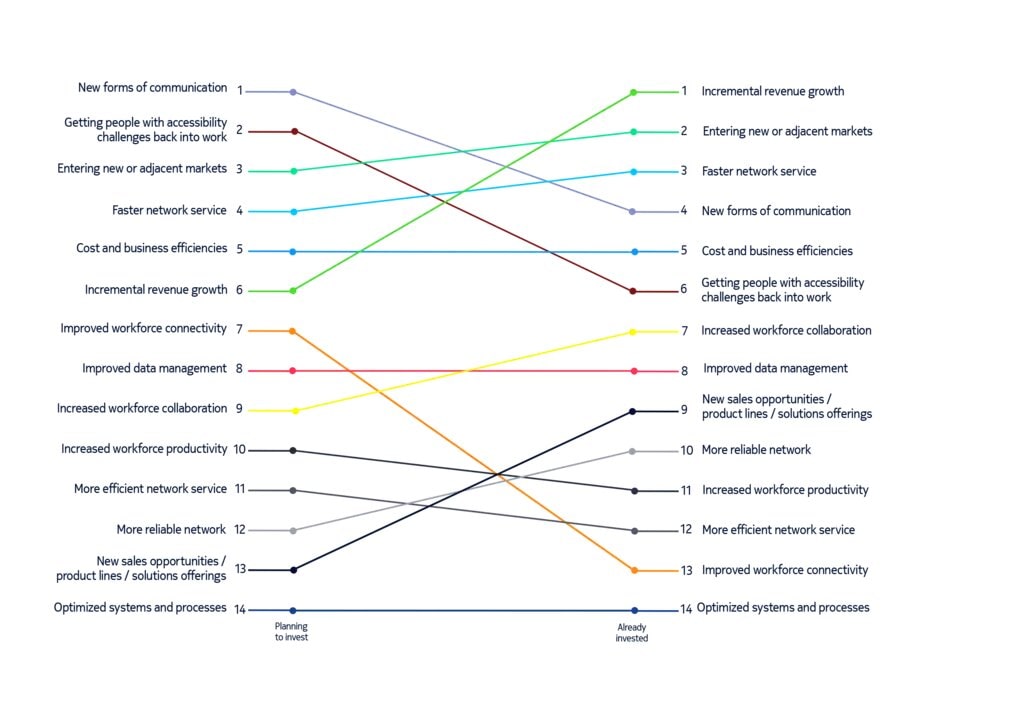
5G is a key tool for industry 4.0 acceleration, and the companies most advanced in their digitalization journeys are likely to be most mature when it comes to 5G, which is one of many digitalization aspects fueling growth and positive business outcomes. However, these findings show that the companies who are most 5G mature, and therefore likely also the most advanced in their digital transformation, are showing the highest impact in overall business performance. This suggests that companies which are delaying their 5G implementation may be missing out on important benefits, including the ability to overcome the challenges of the ongoing pandemic. That correlation was also evident in sub-categories: both the market (Saudi Arabia) and the industry (healthcare) with the highest proportion of 5G mature companies also had the largest share of growing companies in each case (83% and 80% respectively, compared to an overall average of 73%).
But while success is evident, even the most advanced industries are only scratching the surface of what’s possible.
“While many companies evidently see 5G as a technology for the near future, deployment varies by organization, industry and geography,” says Raghav Sahgal, president, Nokia Enterprise. “As our research shows, most organizations are at the Implementation stage – for most, this means trials, pilots or early stage deployments, for example, in mining applications to improve the safety of workers, in power utilities remote control of physical assets to avoid wildfire ignition, or in manufacturing supply chain resilience. Yet, we still have to realize the true breadth, depth and potential of 5G.
"But this doesn't mean organizations have to wait to reap the benefits. Those who have already prioritized and begun deployment of private 4.9G within their business appear to be deriving clear operational benefits today. We believe this demonstrates the importance of linking 5G as a technology to broader business outcomes. If an organization aims to capture revenue growth at some point, it needs to reinvent itself and look for new business and operational models, because an old one can only grow so far. By tying those business objectives to technology, the organization will set itself up for more sustained success.
"More importantly, becoming a 5G mature organization requires a strategic and holistic approach to planning and investment, prioritizing and converging IT and operational technology (OT) departments, which are often working in silos within an enterprise."