Pushing the boundaries of technology has always been part of the Nokia Bell Labs DNA. Bell Labs breakthroughs ushered in the semiconductor age and defined the fundamental laws of communication. Now, as pioneers and technology leaders in space communications, we are applying this same intellectual rigor and creativity to pave the way for exploration of other planets and moons.
Nokia Bell Labs delivered the first cellular network to the Moon, and we will incorporate high-speed communications capabilities in the next-generation spacesuits for Artemis III, the first crewed mission to the lunar surface since Apollo 17. But these two endeavors are only starting points. We envision a rapidly evolving and growing space economy enabled by our advanced communication solutions. Our networks will facilitate scientific discovery, support commercial activities, and help pave the way for a safe and sustained human presence on the Moon and Mars. Working with government and commercial partners, Nokia Bell Labs is creating the networking blueprint, defining a roadmap of technological advances and building solutions that will provide the foundational infrastructure and services for future space missions and programs.
Spacesuit connectivity on Artemis III
The first astronauts to set foot on the Moon in more than 50 years will communicate over a Nokia Bell Labs network. We have partnered with Axiom Space to deliver a spacesuit-integrated communications system that will allow Artemis III astronauts to communicate while they explore the lunar surface. This historic mission will not only mark humanity’s return to the Moon, but it will also serve as a key test of Nokia Bell Labs’ advanced space-based networking solutions, proving cellular technologies can meet the communications needs of human beings exploring the Moon and Mars.

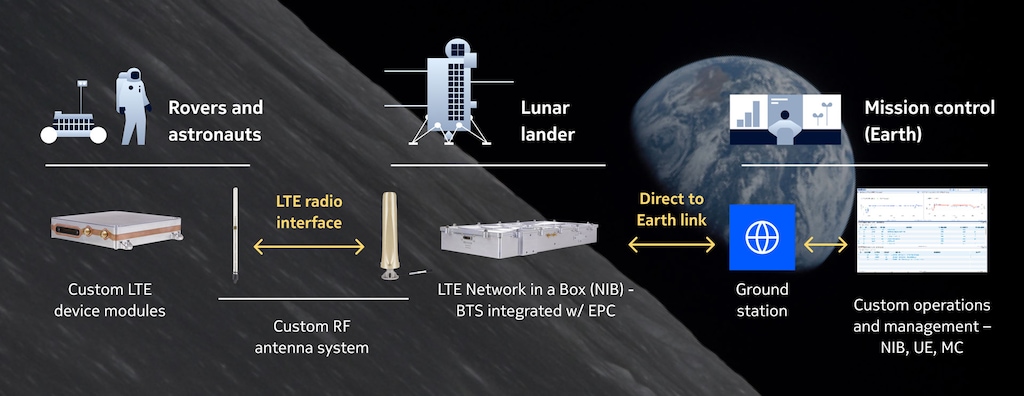
Axiom Space’s Axiom Extravehicular Mobile Unit (AxEMU) spacesuits will be equipped with Nokia Bell Labs’ device modules that will connect to our 4G/LTE network on the Artemis III human landing system (HLS). The HLS will, in turn, relay real-time HD video, telemetry data and voice communications to NASA Mission Control via a direct-to-Earth link.
The future of communications beyond Earth
A renewed global interest in exploring and inhabiting the Moon and Mars is contributing to the rapid growth of the space economy. Advanced communication infrastructure will be crucial to humanity expanding its presence in space. Future missions will bring an ever-increasing number of robots, vehicles, habitats and other payloads to the lunar and Martian surfaces. Future interplanetary commercial operations will deploy infrastructure, drill for resources and create vast sensor grids. And astronauts will need to communicate and share information with one another and mission controllers on Earth as they probe deep into the canyons, craters and undiscovered regions of the Moon and Mars. Nearly every single aspect of this future space economy will require connectivity to function.
Nokia Bell Labs is looking decades into the future. We are working with government agencies like NASA and DARPA, as well as leading commercial space companies to do the advanced planning, design and development for the underlying network systems that will be critical to humanity’s long-term presence on the Moon and other planets.
The first cellular network on the Moon
As part of NASA’s Tipping Point initiative, Nokia Bell Labs delivered the first cellular network to the Moon on March 6, 2025, during Intuitive Machines’ IM-2 mission to the lunar south pole. The mission concluded early due to the configuration of the IM-2 lander, preventing the deployment of its solar panels and limiting available power, but Nokia successfully validated key aspects of the network’s operation. By achieving these milestones, Nokia took significant steps toward proving that cellular technologies can meet the critical communications needs for future missions to the Moon and Mars.

Taking 4G further
While the Lunar Surface Communications System (LSCS) is a 4G/LTE system at its heart, it is unlike any cellular network on Earth. Nearly two decades of Bell Labs research and innovation have gone into entirely reconceptualizing a terrestrial network to meet the unique parameters of a lunar mission. We pushed the boundaries of automation, optimization, miniaturization and integration by combining the radio, base station, routing, security and core network elements into a single highly resilient “network in a box” that can be easily installed on a lunar lander, rover or habitat. We overhauled its system software to create a fully autonomous network, capable of self-deploying, self-configuring and self-healing. And we designed multiple hardware and software redundancies and failover mechanisms to alleviate and recover from any potential hardware and electronic failures caused by cosmic radiation. The LSCS is more than the “network in a box”; we have developed device modules and antennas along with custom operations and management software. Together all these components form an end-to-end solution creating a cellular network for machines and people to communicate while exploring and studying the lunar surface.
Each of the LSCS components has been carefully engineered to withstand the dynamic stresses of launch, spaceflight and landing as well as operate in the extreme environmental conditions on the Moon’s surface. It meets the rigorous size and weight limitations of spacecraft payloads, and its power consumption has been optimized to easily deal with low and intermittent power supplies. As we look toward future missions, Nokia Bell Labs will evolve the LSCS to support 5G and the unique requirements of Mars missions.
Read more
Our history in space
IM-2 won’t be Nokia Bell Labs’ first foray into the heavens. Bell Labs provided systems analysis and engineering for every crewed US space program from Mercury to Apollo. In 1962, Bell Labs and NASA launched into orbit Telstar 1, the first communications satellite capable of relaying TV signals between Europe and North America. In 1964, Bell Labs researchers – who became Nobel laureates – Arno Penzias and Bob Wilson discovered the cosmic microwave background radiation left over from the Big Bang, confirming the now predominant theory on the origins of the universe. Bell Labs researchers have always had an intense scientific curiosity that has led to some of the greatest innovations and discoveries known to humankind.